Climate Smart Agriculture Adapting to Global Warming
Emphasizing the need to convince the government that we can produce enough food using natural farming, he called for using climate-tolerant crop varieties like the Swarna rice. This variety of rice, considered tolerant to water logging, used to be grown in India in the past.
The important mitigation options include:
- Efficient water and nutrient management options to enhance use efficiency
- Evaluation of carbon sequestration potential of different land use systems
- Understanding opportunities offered by conservation agriculture and agro-forestry
- Identifying cost-effective methane emission reduction practices in ruminants and in rice paddy
- Encouraging Climate Smart Agriculture Farms for high yielding vegetables, fruits, flowers and other cash crops for achieving higher productivity,
Certainly! Let’s explore the importance of Climate-Smart Agriculture (CSA):
Definition and Goals:
CSA is an approach that guides actions to transform agri-food systems toward green and climate-resilient practices.
It supports internationally agreed goals such as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the Paris Agreement.
The three main objectives of CSA are:
- Sustainably increasing agricultural productivity and incomes.
- Adapting and building resilience to climate change.
- Reducing and/or removing greenhouse gas emissions, where possible.
Why Is CSA Important?
Environmental Resilience: CSA helps farmers adapt to changing climate conditions by promoting practices that enhance resilience. These practices include crop diversification, soil conservation, and water management.
Sustainable Productivity: By adopting CSA practices, farmers can improve yields while minimizing negative environmental impacts.
Reducing Emissions: CSA contributes to global efforts to mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture.
Food Security: Strengthening food security is a critical goal. CSA practices enhance productivity, ensuring a stable food supply.
Livelihoods: CSA benefits smallholder farmers by providing them with sustainable income opportunities.
Business Opportunities: CSA opens up new business avenues related to climate-smart technologies and practices. We from Make My Tree Pvt Ltd is focusing on establishing Climate Smart Agriculture and Farms.
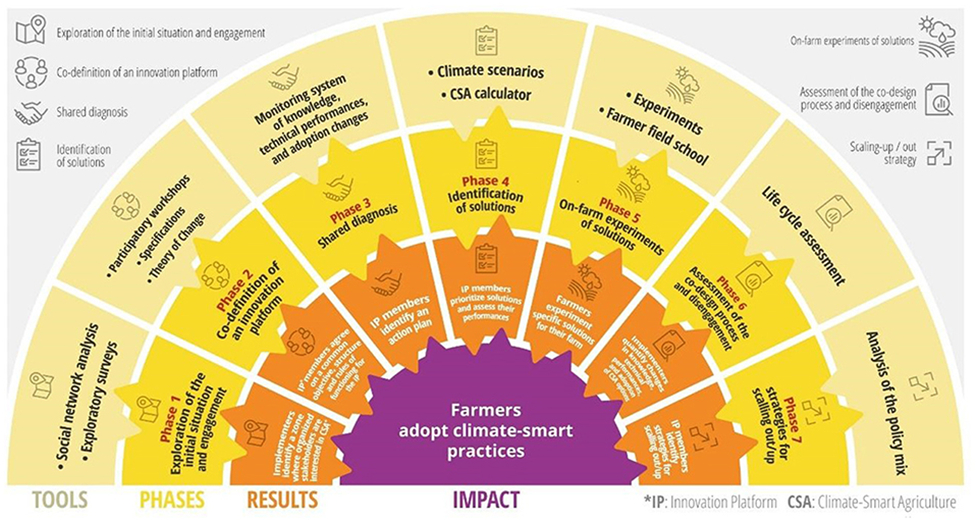
Implementation:
CSA practices vary based on local factors such as socio-economic conditions, environmental context, and climate change impacts.
Key actions for implementing CSA include:
- Expanding the evidence base for CSA.
- Supporting enabling policy frameworks.
- Strengthening national and local institutions.
- Enhancing funding and financing options.
- Implementing CSA practices at the field level.
In summary, CSA is crucial for building sustainable food systems, protecting the environment, and improving livelihoods. By scaling up CSA practices, we can address climate challenges and create a better future for all. If you have more questions or need further information, feel free to ask!
The need for Climate Smart Agriculture?
Climate-smart agriculture and innovative smart farming technologies such as hydroponics, Aeroponics, and aquaponics are essential for addressing critical challenges in agriculture. Let’s delve into why they are crucial:
Climate-Smart Agriculture (CSA):
- Urgent Challenges: Agriculture faces three urgent challenges:
- Livelihood Improvement: Creating better livelihoods for farmers.
- Efficient Agriculture: Enhancing agricultural efficiency.
- Carbon Sequestration: Contributing to carbon sequestration.
- Importance of CSA:
- Farmers’ Livelihoods: 2.5 billion people depend on agriculture for their livelihoods.
- Global Jobs: The sector represents 35% of global jobs.
- Environmental Impact: Agriculture accounts for over 30% of greenhouse gas emissions, 80% of tropical deforestation, and 70% of freshwater withdrawals.
- Solution: Climate-smart agriculture approaches address these challenges by promoting sustainable practices, resource efficiency, and resilience
Hydroponics and Aeroponics:
- Resource Efficiency: These soil-less techniques optimize resource usage:
- Water: Recirculated water minimizes wastage.
- Nutrient Delivery: Precise nutrients enhance productivity.
- Year-Round Production: Regardless of weather, they allow continuous cultivation.
- Reduced Pesticide Use: Controlled environments minimize chemical pesticide needs.
- Space Optimization: Vertical farming maximizes land use.
- Mitigating Soil Erosion: Prevents soil degradation.
- Climate Resilience: Stability in changing climate patterns
- Resource Efficiency: These soil-less techniques optimize resource usage:
Aquaponics:
- Symbiotic System: Combines aquaculture (fish farming) with hydroponics.
- Benefits:
- Nutrient Recycling: Fish waste fertilizes plants.
- Water Conservation: Recirculating water reduces consumption.
- Diverse Yield: Both fish and crops can be harvested.
- Climate Adaptation: Resilient to weather fluctuations.
- Promotes Sustainability: Efficient use of resources and reduced environmental impact.
In summary, adopting climate-smart practices and leveraging smart farming technologies like Hydroponics, Aeroponics, and Aquaponics is crucial for sustainable agriculture, farmer well-being, and global food security.